What is the Gasser Ganglion Treatment?
Gasser Ganglion ballon compression and radiofrequency and pulsed radiofrequency treatments are minimally invasive procedures in which the Gasser ganglion (trigeminal nerve cluster) is stimulated with pressure or with electrical impulses and then treated with heat or eletric stimulation.
 How does Gasser Ganglion treatment work?
How does Gasser Ganglion treatment work?
During the treatment, the pressure or radiofrequency energy selectively deactivates the nerve cells of the Gasser ganglion, thereby reducing or eliminating the transmission of pain impulses. In case of pulsed radiofrequency the nerve cells are not lesioned by heat, but rather „reprogrammed”, modulated.
In which diseases/conditions can Gasser Ganglion treatment be used?
- Trigeminal neuralgia (facial nerve pain) – with high efficacy
- Certain selected cases of atypical facial pain
What are the contraindications of the procedure?
Severe bleeding disorders, local or systemic infection.
What to expect during the procedure?
- The procedure takes place in an operating room, under sterile conditions. Only one needle passes through the skin, which is positioned at the Gasser Ganglion with the help of X-ray guidance.
- The procedure is performed in a combination of anesthesia and local anesthesia.
- The duration of the procedure is usually 20-60 minutes.
- Return home is usually possible a few hours after the procedure.
What happens after the procedure?
- It takes about 3-5 days after the procedure until the final effect is achieved in case of radiofrequency ablation.
- Typically ballon compression provides immediate effect
- Pulsed radiofrequency treatment can take up to one month to see full effect.
- Normal daily activities can be resumed from the day after the procedure.
What does the complete treatment consist of?
• Treatment usually consists of one procedure. However, if years later the pain returns, the procedure can be repeated.
How long will the benefit last?
The duration of improvement in function and pain relief may vary from person to person. Generally, the procedure provides a solution for many years. In some patients, the effect may last even longer, while in others, symptoms may recur over time. The procedure can be repeated with similar success and risk.
Side effects of Gasser Ganglion treatment
With pulsed radiofrequency no weakness or sensory loss of any kind is expected.
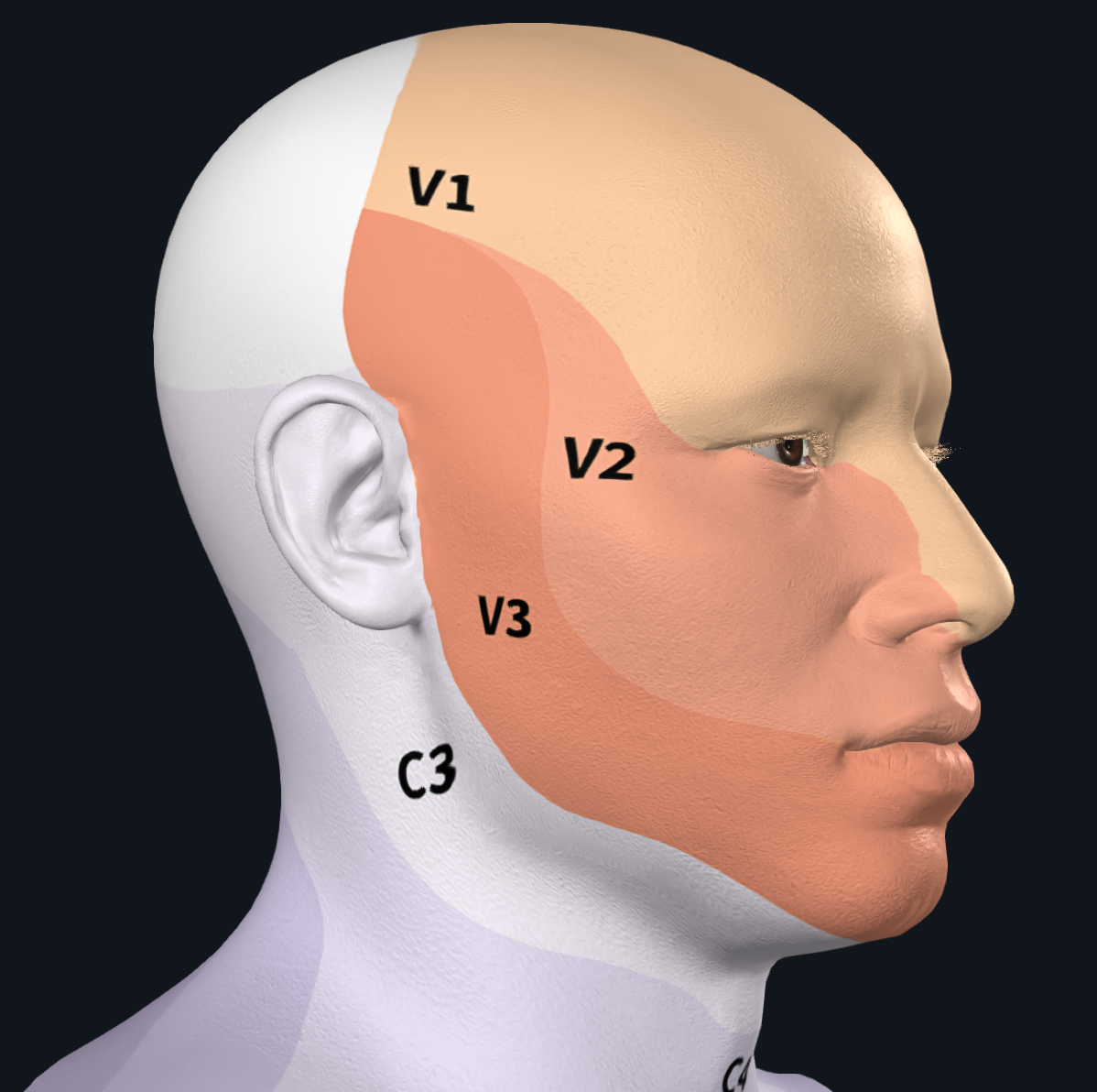
With radiofrequency or ballon compression there may be some weakening of the muscles responsible for chewing the affected side, if the V3 branch was also treated. However, this usually does not cause a problem because the well-functioning chewing muscles on the other side easily compensate for the deficiency. This does not occur when treating the V1, V2 areas. Small numb areas on the face may occur, which may last for shorter or sometimes longer periods. This typically does not bother patients much.
Possible risks and complications
- Uncommon: cornea insensitivity can happen especially if the V1 branch is treated
- Extremely rare ( < 1:100 000) : infection, bleeding, temporary eye movement disorders, intracranial bleeding, retroorbital bleeding.(Kanpolat et al. 2001)
- Unknown, extremely rare: Postprocedural diplopia (usually temporary)
Source:


