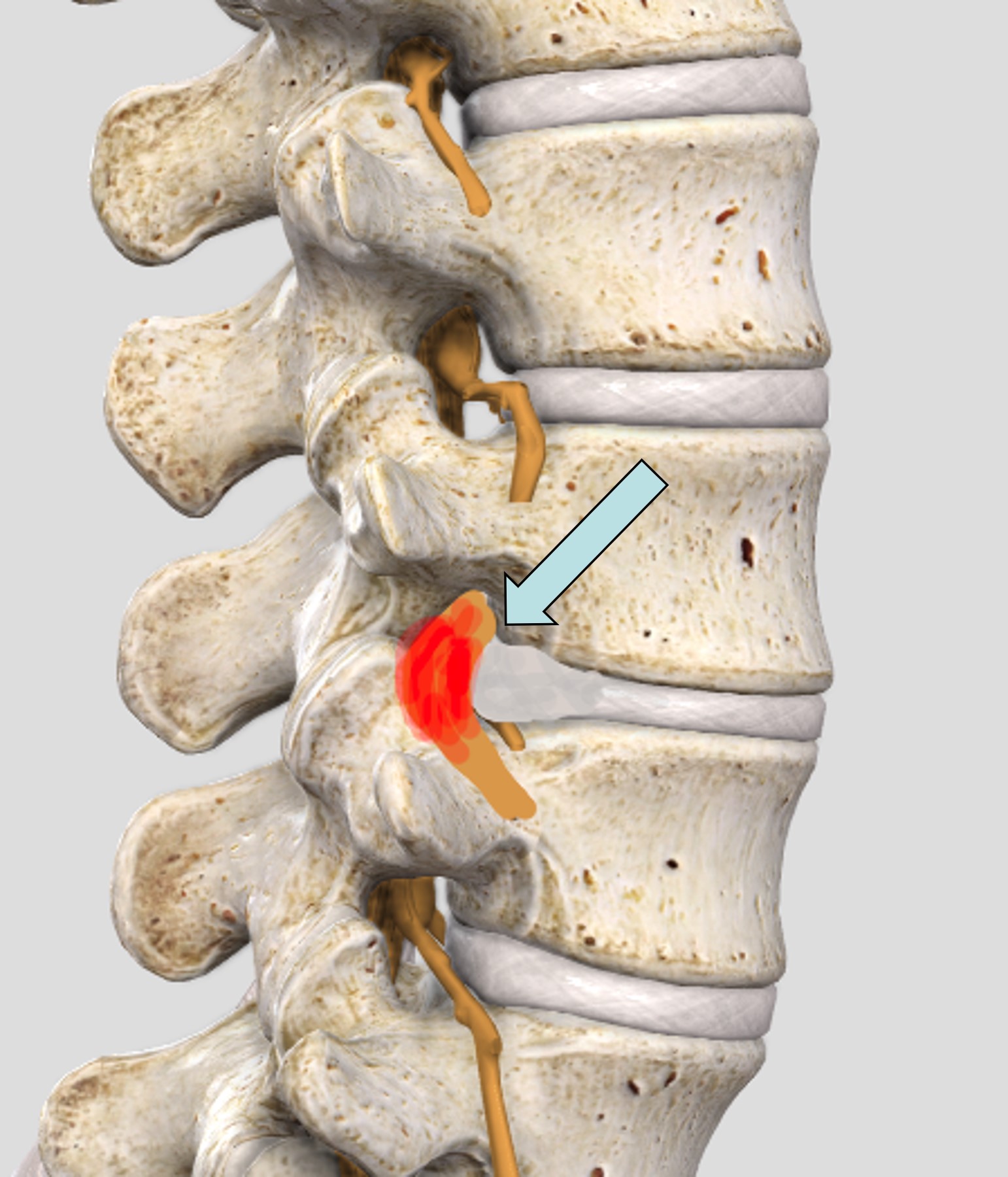
Radicular compression, radiculopathy, and radiculitis refer to conditions affecting the exiting nerve roots. The nerve root is most commonly compressed by the bulging of a spinal disc, but other tissues can also narrow the space through which the nerve exits the spinal canal. Radiating pain into the extremities is the most common symptom, but numbness or weakness in the limb may also occur. Based on symptoms, physical examination, and MRI findings, the treating physician determines which nerve root is affected and decides on the appropriate course of action.
In simpler cases, symptoms may improve spontaneously or with the help of exercises. For more stubborn cases, minimally invasive interventions range from PRP therapy to stem cell treatments, simple epidural injections, and even epidurolysis. These procedures can be most accurately performed under X-ray guidance, and in some cases, ultrasound or CT guidance may also be suitable. In severe cases, where motor function deteriorates, or if the patient experiences loss of sensation in the perianal region, difficulty controlling bowel or bladder, urgent consultation with a neurosurgeon is recommended.